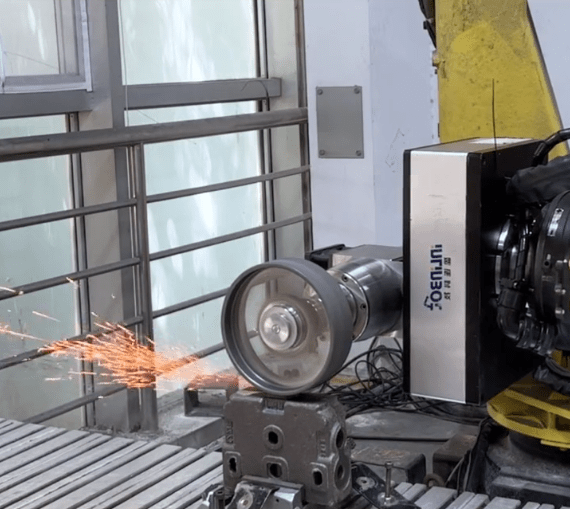
The purpose of grinding a component after its production from conventional machine tools serves several important functions in the manufacturing process:
Precision and Tolerance:
Grinding allows for achieving tight tolerances and high precision in the dimensions of a component. This is crucial for ensuring that the final product meets the required specifications and fits perfectly within the assembly.
Surface Finish:
Grinding improves the surface finish of a component, providing a smoother and more refined surface. This is important for both functional and aesthetic reasons, especially in applications where a polished or smooth surface is essential.
Removal of Imperfections:
Components produced through conventional machining processes may have imperfections, such as burrs, tool marks, or irregularities. Grinding helps remove these imperfections, resulting in a cleaner and more uniform appearance.
Dimensional Accuracy:
Grinding allows for the fine-tuning of dimensions, ensuring that the final component matches the intended design specifications. It helps achieve the desired shape and size with high accuracy.
Final Machining Operations:
Grinding is often used as a final machining step after other conventional machining processes like turning, milling, or drilling. It serves as a finishing operation to achieve the desired dimensions and surface quality.
Material Removal:
In cases where excess material needs to be removed from a component, grinding provides an efficient method for material removal. This is particularly relevant when dealing with hard or heat-treated materials that are challenging to machine using traditional methods.
Improved Mechanical Properties:
Grinding can enhance the mechanical properties of a component, such as hardness and wear resistance. Heat generated during the grinding process can also contribute to beneficial changes in the material’s microstructure.
Specialized Shapes and Profiles:
Grinding allows for the creation of specialized shapes, profiles, or features that may be challenging or impossible to achieve with conventional machining techniques. This is especially valuable in industries where intricate or complex components are required.
Tool and Die Production:
In tool and die manufacturing, grinding is often used to produce molds, dies, or cutting tools with high precision and durability. The tool and die industry relies heavily on grinding for creating sharp cutting edges and intricate shapes.
Batch Consistency:
Grinding ensures batch-to-batch consistency in mass production. It helps maintain uniformity across multiple components, meeting quality standards and reducing variations in the final products.