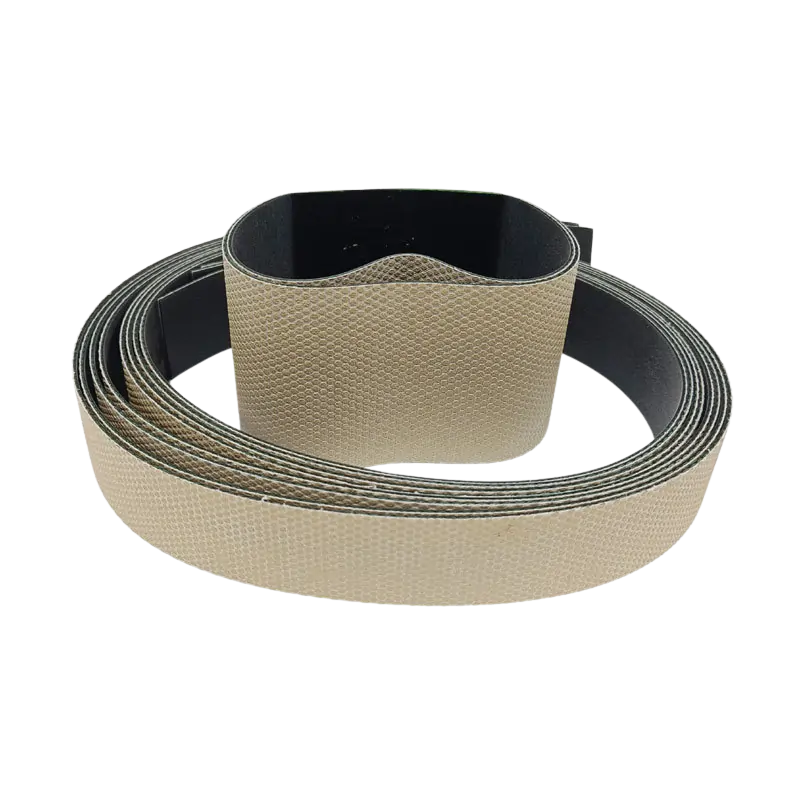
Diamond Sanding Belts
Premium Diamond and CBN Sanding Belts
Both in Electroplated Diamond Sanding Belts and Diamond Resin Belts
Wide Range of Applications: marble, stone, ceramic tiles, glass, quartz glass, optical glass , carbide coatings, ceramic coatings, titanium alloys, tungsten carbide, hard alloys, high-temperature alloys, single crystal silicon, polycrystalline silicon, fiberglass, and carbon fiber composite materials.
High Efficiency & Flexible: superior grinding and polishing with excellent flexibility for complex surfaces
Description
Diamond Sanding Belts are coated abrasives where synthetic diamond abrasive grains are bonded to a flexible, bendable substrate (such as nylon cloth) using adhesives. Compared to conventional abrasive belts, diamond sanding belts combine the “hardness” of superhard materials with the “flexibility” of coated abrasives,offering excellent grinding performance and adaptability.
Features and Advantages of Diamond Sanding Belts
Sharp and Durable: Diamond sanding belt possesses sharp cutting edges and extended service life. They outperform silicon carbide and aluminum oxide belts in longevity.
High Grinding Efficiency: The orderly arrangement of grinding units creates large chip spaces, aiding heat dissipation and improving processing quality and efficiency.
Good Flexibility: The flexible substrate allows diamond sanding belts to adapt to various complex surface contours.
Environmental Benefits: Reduced dust and noise during operation contribute to significant environmental advantages.

Structure of Flexible Diamond Belt
Diamond sanding belts generally consist of three components:
Substrate: The carrier for the abrasive and adhesive, providing flexibility. Common substrates for diamond abrasive belt include cloth, composite materials, non-woven fabrics, and polyester films. Key performance indicators include radial and weft tensile strength, elongation rate, and mesh density for woven substrates.
Abrasive: The primary grinding material, with synthetic diamond being the abrasive of choice. Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) abrasives can also be used to create CBN sanding belts. Performance indicators include abrasive grain size, compressive strength, impact toughness, grain shape, and abrasive density.
Bonding Agent: Acts as a bridge between the abrasive and the substrate, providing structural integrity and strength. Cast Grind Solutions offers two types of bonding agents: electroplated nickel bond diamond sanding belt and resin bond diamond sanding belt.
Types of Diamond Abrasive Sanding Belts by Bonding Process
Electroplated Diamond Sanding Belts:
Electroplated diamond belts are manufactured using electrochemical methods to uniformly distribute diamond particles onto the substrate, typically using nickel as the medium. The diamond is deposited in two layers onto a metal mesh and bonded to a flexible cloth backing to form continuous loops of varying sizes.
Applications of Electroplated Diamond Belt
Grinding: Ideal for hard materials like ceramics, glass, and stone, as well as hard alloys, tool steels, and high-speed steels.
Polishing: Removes surface burrs, scratches, and irregularities, making metal surfaces smooth and shiny.
Lapping: Perfect for polishing glass, gemstones, and optical components to achieve ultra-smooth finishes.
Resin Bonded Diamond Sanding Belts:
Utilizing resin as the bonding agent, diamond resin belts feature a multi-layered diamond abrasive structure with an open pattern that resists clogging. They offer high sharpness, durability, and uniform grinding effects. Suitable for both dry and wet applications.
Applications of Diamond Resin Belt
Woodworking: Efficient for cutting and polishing hardwoods like oak.
Non-Metallic Materials: Effective in cutting and polishing stones such as marble and granite.
Metalworking: Used for grinding and polishing metal surfaces to achieve desired surface roughness.
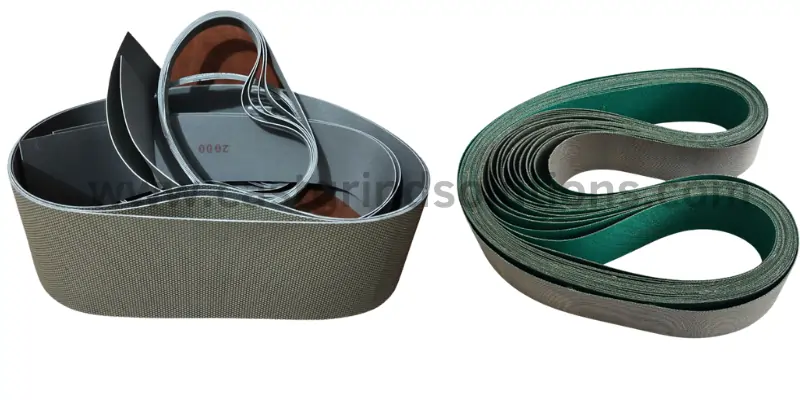

Technical Specifications
Abrasive Type: diamond abrasive and CBN(cubic boron nitride) abrasives
Bond Types: electroplated diamond abrasive sanding belts, diamond resin sanding belts
Diamond Sanding Belts Grit Range:
- electroplated diamond belts grit range :60#-5000#
- diamond resin bonded sanding belts grit range: 60#-7000#
Diamond Sanding Belts Length :200mm-5000mm
Diamond Abrasive Belts Width: 5mm-400mm
Dry/ Wet Grinding: both dry and wet grinding and polishing
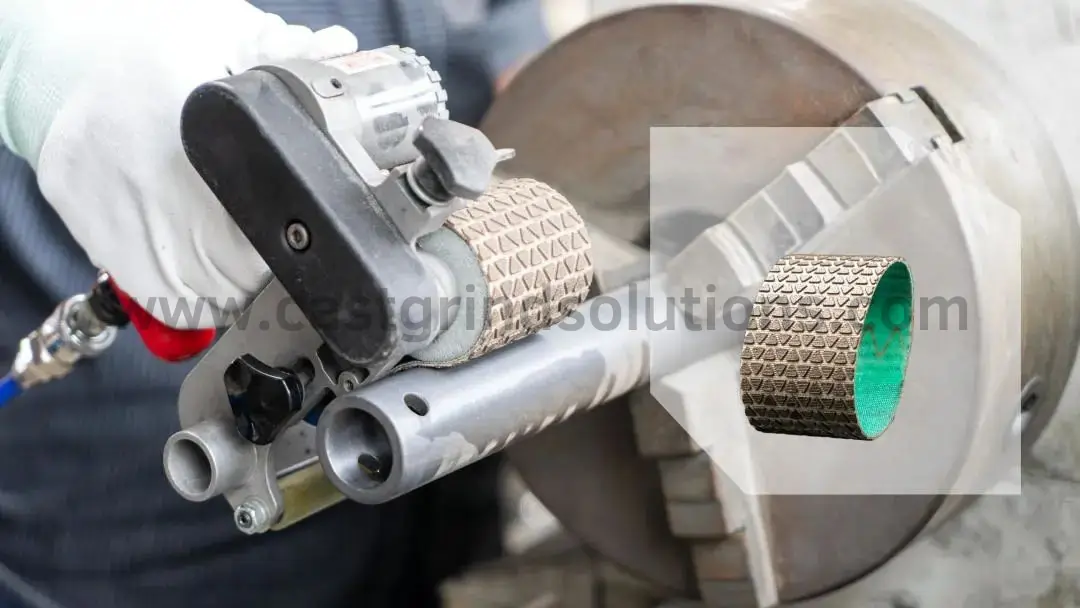

Four Key Advantages of Cast Grind Solutions’ Diamond Grit Sanding Belts
Durability and Stability: Premium backing materials and diamond abrasives ensure dimensional and performance stability.
Strong and Reliable: Special joint techniques enhance durability and safety.
High Grinding Efficiency: Proprietary abrasive patterns improve sharpness and longevity.
Strict Quality Control: Each diamond grit sanding belt undergoes rigorous quality inspections to ensure superior product standards.
Customization Process for Diamond Sanding Belts
Cast Grind Solutions offers custom diamond sanding belts. Our customization services include:
- Two Bond Types: including electroplated diamond sanding belts and diamond resin-bonded sanding belts.
- Two Abrasive Types: diamond sanding belts and CBN (cubic boron nitride) abrasive sanding belts;
- Diamond Pattern Shapes: You can either choose from our existing patterns or request custom designs for your specific needs.
- Softness and Hardness: We can customize the softness or hardness of the diamond sanding belts. For example, ultra-thin and flexible micro-mesh diamond belts are suitable for polishing surfaces with uneven contours.
- Custom Diamond Belt Size and Grit: We offer a range of grits from 60# to 7000#, meeting requirements from rough grinding to ultra-fine polishing. Custom sizes can be made as per your specifications.
- Velcro-backed Diamond Sanding Belts: like flexible diamond drum belts work with expandable rubber drums , suitable for wet grinding a variety of substances.
If you are unsure about your specific needs, feel free to contact us. We will work with you to provide the most suitable diamond sanding belt solution for your applications.
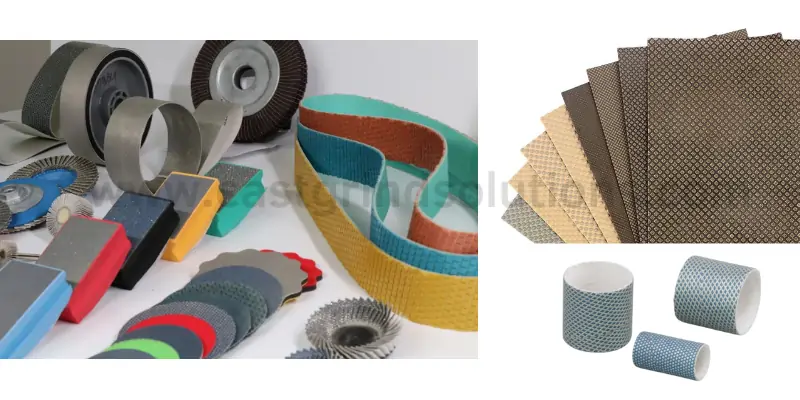

Features
Coating Patterns on Diamond Sanding Belts
The high grinding efficiency of diamond abrasive belts is attributed not only to the hardness of diamond abrasives but also to the unique coating patterns. Cast Grind Solutions offers diamond abrasive belts with various coating patterns, affecting the distribution of diamond particles. These diamond belt micro-patterns optimize the belt-to-workpiece contact, enhancing grinding precision and surface quality.
The structured abrasive units, covered with diamond clusters, create distinct grinding mechanisms. The gaps between units facilitate chip removal, improve airflow for heat dissipation during dry grinding, and promote coolant flow in wet grinding, enhancing processing quality and the longevity of the diamond belt sander.
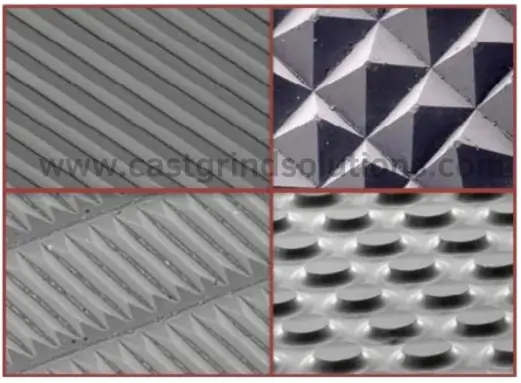
Grinding Characteristics of Diamond Abrasive Belts
Compared to Diamond Grinding Wheels, diamond sanding abrasive belts offer flexibility, making them ideal for processing curved surfaces of hard, brittle materials like automotive windshields. For example, straight-edge grinding of glass with wheels requires multiple tools, while cross-belt machines with just two electroplated diamond belts can perform both straight and curved edge grinding efficiently, suitable for industrial production lines.
Usage Guidelines for Diamond Sanding Belts
Select the Right Diamond Belt: Choose appropriate size and diamond grit based on the material hardness and grinding requirements.
Proper Use and Maintenance: Maintain correct tension and grinding pressure to avoid excessive wear. Regularly clean the diamond belts surface to remove debris.
Avoid Overloading and Folding: Prevent damage to the diamond abrasive layer.
Safety Precautions: Do not touch the diamond abrasive layer when the belt is rotating. Use protective gear like goggles and masks during operation.

Application
Applications of Diamond Abrasive Sanding Belts
Glass Industry
Diamond sandpaper for belt sander are widely used in the glass industry, especially for edging automotive windshields, architectural glass, and crystal glass. The automotive windshield manufacturers are major clients for large diamond grit sanding belts. These diamond finishing belts are used with both standalone manual cross-belt grinding machines and automated production lines, such as ASH-TON’s horizontal machines, LISSEK’s vertical machines, and large-scale sanding edge equipment assembled by OEMs. As the automotive industry continues to grow, the demand for diamond coated abrasive belts will also increase.
Super-Hard Metal Alloy Coatings
Diamond sanding belts systems can replace diamond grinding wheels for grinding and polishing processes. These systems are commonly used in the thermal spray industry, hydraulic cylinder production, turbine blade production and repair, and more. For instance, in grinding large tungsten carbide rollers in steel factories, users typically require a roughness of 3.0μm to 4.2μm. If diamond grinding wheels are used, the process takes around 8 hours to complete, but with diamond abrasive belts, all work, including setup, can be finished in under an hour. This leads to significant time, energy savings, and reduces environmental pollution.

Silicon Ingot Grinding and Chamfering
Silicon ingots require surface grinding before slicing to remove etched cracks, which significantly increases yield when using a diamond wire saw for slicing. A single grain size diamond sanding belt can perform all processes, achieving up to three times the speed of conventional methods and a surface roughness of Ra 0.07. This results in better efficiency and automated handling in silicon ingot processing.
Ceramic and Stone Applications
To overcome the wear resistance and corrosion issues of traditional metal valves, the use of ceramic valves has become more popular. However, ceramics’ inherent brittleness and difficulty in processing have limited their application. With the advent of diamond abrasive sanding belts, the advantages of ceramic valves are more apparent, and their use is growing in industries like valve manufacturing. Additionally, diamond sanding belts are widely used in the surface and edge polishing of engineering stones such as marble and granite.





