Description
A diamond dresser is a tool used in manufacturing and machining processes, particularly in grinding operations. It’s designed to dress or true a grinding wheel, which means it helps to restore the wheel’s shape and cutting efficiency by removing dull abrasive grains and reorganizing the remaining ones.
3 Types and Uses of Diamond Dressers
Single Point Diamond Dresser:
Mainly used for dressing grinding wheels on general-purpose grinding machines, such as cylindrical grinders, centerless grinders, surface grinders, internal grinders, and parallel grinding wheels.
Diamond Forming dresser (Chisel Dressers):
Primarily used for dressing profile grinding wheels on CNC grinders, including beveled wheels, single bevel, double bevel, and butterfly wheels for precision dressing.
Dressing Tools for Rough Grinding (Stone dresser Tools):
Available in two shapes, square and round, these are used for rough grinding wheel dressing on general grinding machines, such as 46# and 60# grinding wheels.
Currently, the most common tool in use is the single-point diamond dressers;, accounting for approximately 60%-70% of the total usage. Multi-stone dressers, used mainly for rough grinding, make up about 40%-50% of the usage. Chisel diamond dressing tools, are typically custom-made based on client drawings and requirements. Our distributors mainly sell single-stone diamond dressers and multi-stone dressers. For Forming dresser, please contact our technical team to finalize drawings and usage parameters for customization.

Types and Characteristics of Diamond Materials Used in Grinding Wheel Dressing Tools
Many of our dealers and customers know the different shapes of diamond grinding wheel dressers, but are not familiar with the types of diamond materials used. Here, we elaborate on the types and characteristics of these materials:
Natural Diamond:
Natural diamonds are categorized into two main types: those used for jewelry and those used for industrial purposes. Jewelry-grade natural diamonds are characterized by their transparent color and high precision, while industrial-grade natural diamonds can range from light to coffee-colored hues. The lighter the color of an industrial diamond, the higher its grade. The quality of natural diamonds is assessed based on four criteria: weight, color, clarity, and structure.
- Weight: refers to the size of the diamond.
- Clarity: indicates the amount of internal impurities; more impurities mean poorer quality.
- Structure: pertains to the presence or absence of cracks, their size and quantity, and the presence of bubbles or other inclusions. A higher number of cracks and bubbles increases the likelihood of chipping or breaking during processing or use.
Before the maturation of artificial diamond production techniques, all grinding wheel dressing tools utilized natural diamonds. In 2011, we first introduced artificial diamonds, and by 2013, due to the scarcity and rising costs of natural diamond raw materials, we shifted a significant portion of our less precision-demanding diamond wheel dressers, to artificial diamonds. This transition has been ongoing for over ten years, reducing our reliance on natural diamonds from 100% to approximately 20%.
Currently, natural diamond dressers are primarily used for single point dressers and chisel diamond dresser in industries requiring high precision and fine-grained grinding wheels, as well as components with stringent surface finish and stability requirements.
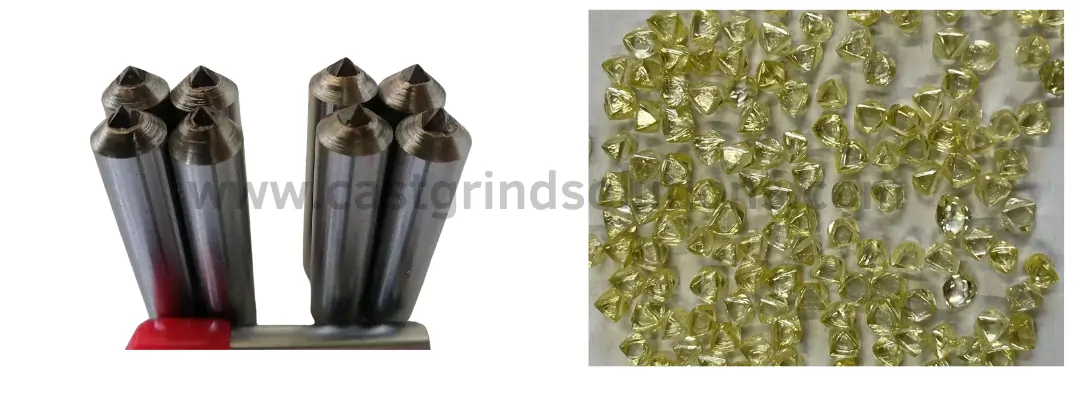

Synthetic Monocrystalline Diamond
The second type of diamond material is synthetic monocrystalline diamond. This material is the most commonly used in single-point diamond pens, accounting for 60-70% of the usage. These diamonds typically have a light yellow to deep yellow color. Large grain synthetic monocrystalline diamonds are predominantly used for single point diamond pens, whereas smaller grains are utilized for multi-point diamond pens.
The key features of synthetic monocrystalline diamonds include their relatively uniform shape and the fact that a lighter color indicates higher purity and better quality. The evaluation criteria for synthetic monocrystalline diamonds are also based on three factors: weight, clarity, and structure.
- Weight: denotes the size of the diamond.
- Clarity: measures the amount of internal impurities; more impurities equate to lower quality.
- Structure : involves the presence or absence of cracks, their size and quantity, and the presence of bubbles or other inclusions. A higher number of cracks and bubbles can lead to chipping or breaking during processing or use.
We began mass-producing diamond dressers using this diamond abrasive in 2013, accumulating extensive experience in both production and application over the past decade. Our R-series single-point dressing tools utilize this synthetic monocrystalline diamond, ensuring stable performance without inconsistencies between different units. Additionally, these welded diamond dressing tools achieve precision close to that of natural diamonds, capable of dressing grinding wheels ranging from 60# to 80#, with surface finishes as fine as Ra0.8-0.4 um.

Synthetic Polycrystalline Diamond (CVD):
Let’s move on to discuss Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) polycrystalline diamond, a material primarily composed of carbon and other elements. CVD is the production process used for this type of diamond. It is commonly referred to as CVD diamond or CVD polycrystalline diamond. This material comes in two forms: one that is opaque, appearing nearly black under light, and another that is translucent, allowing some light to pass through. However, it is not accurate to judge the quality of CVD polycrystalline diamond solely based on its transparency. For instance, some CVD diamond dressing tools available on the market are translucent but perform poorly due to issues like low hardness or poor durability. Conversely, high-quality CVD dresser tools made by some manufacturers from non-transparent materials can be highly durable and have excellent hardness, even though they are also made from CVD polycrystalline diamond.
CVD polycrystalline diamond is mainly used to manufacture form dressers and Chisel-type diamond tools.
Currently, about 60-70% of form dressing tools and Chisel-type form dressers are made from this material. Its stability is relatively good, although it does not achieve the same level of dressing precision as natural diamonds. However, its cost-effectiveness is significantly higher compared to natural diamonds.
Synthetic Single Crystal CVD Diamond:
Next, we will talk about Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) single-crystal diamond. The term “polycrystalline” implies a composite material made up of multiple elements, while “single-crystal” refers to a material composed of a single element. Natural diamonds are also single-crystal diamonds because they are formed from pure carbon. Therefore, CVD single-crystal diamond and natural diamonds are theoretically the same type of material. The characteristics of CVD single-crystal diamond include being composed of pure carbon, with very good transparency, often appearing light brown or transparent.
This material is also used to manufacture form dressing tools and Chisel edge diamond dressers, currently accounting for approximately 20-30% of the market share for these types of form dressers. It is considered the best alternative to natural diamonds, offering a lifespan that is 40-50% longer than polycrystalline CVD diamond and achieving a dressing accuracy two grades higher. It can be used to dress grinding wheels ranging from 60# to 240# grit, suitable for fine grinding of surfaces with a roughness requirement of Ra0.4μm or less. It is currently the most cost-effective material for form dressing tools and diamond chisel point tools. We began mass-producing this type of CVD single-crystal diamond dressing tool in 2021, and we have accumulated extensive production and application experience. Our CVD single-crystal diamond dressing tool, as a premium product, has gained widespread recognition within the industry.
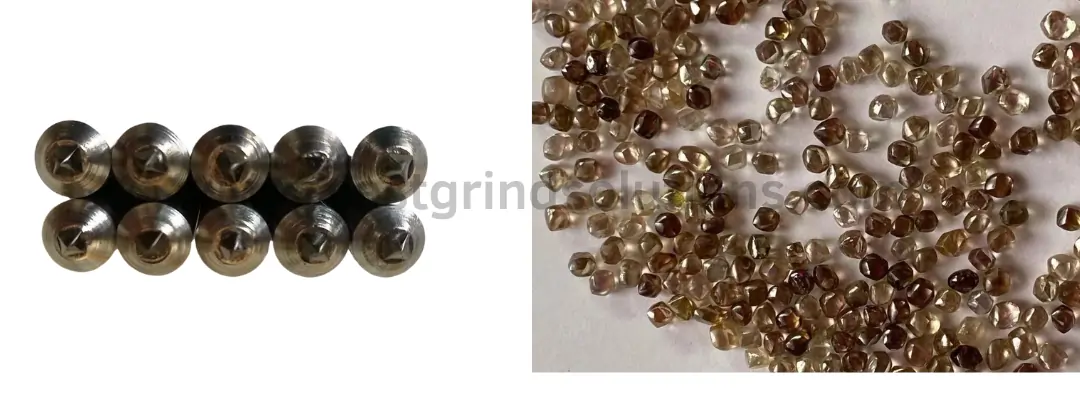
Polycrystalline Diamond (PCD):
Finally, let’s introduce polycrystalline diamond(PCD) which is composed of carbon and other trace elements. This material is typically dark brown or black, remaining opaque even under strong light. PCD diamond is primarily used to make low-cost single-point diamond pens for rough grinding and dressing of smaller-sized grinding wheels, such as those with a diameter of 300mm or less and a grit size of 46#. The diamond part of these diamond pens is triangular, with diameters ranging from 2mm to 4mm. This material accounts for 10-15% of the sales volume of single-point diamond dressers on the market.
If you have any questions regarding diamond materials, please feel free to contact us.
Technical Specifications
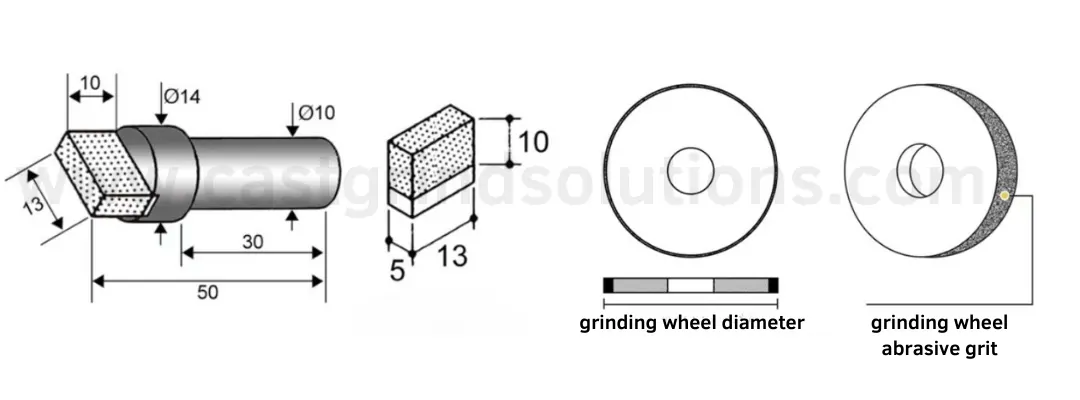
Diamond Stationary Dressers Normal Types Parameters
Single Point Diamond Dresser Normal Types
| Model Type | Weight of Diamond | Dressing wheel size | Dressing wheel grit | Working surface roughness |
| R01 | 0.1 carat | Less than 200mm | 80# | Ra=1-0.4um |
| R02 | 0.2carat | Less than 300mm | 60-80# | Ra=1-0.6um |
| R025 | 0.25carat | Less than 350mm | 60-80# | Ra=1-0.6um |
| R03 | 0.3carat | Less than 400mm | 46-80# | Ra=1-0.6um |
| R05 | 0.5carat | Less than 400mm | 46-80# | Ra=1-0.6um |
| D07 | 0.7carat | Less than 500mm | 46-80# | Ra=1-0.6um |

Sintered Diamond Muti-stone Dressing Tools Normal Types
| Model Type | Weight of Diamond | Dressing wheel size | Dressing wheel grit |
| F50 | 5 carat | Less than 400mm | 46# |
| F65 | 6.5 carat | Less than 400mm | 46# |
| FD100 | 10 carat | Less than 500mm | 46-60# |
| F55T | 5.5 carat | Less than 750mm | 20-60# |
| T800 | 8 carat | Less than 750mm | 46-60# |
Chisel Edged Diamond Radius Dresser Normal Types
| Model Type | Weight of Diamond | Diamond Angle | Diamond Arc | Working surface roughness |
| D2515 | 0.6 carat | 40°-80° | R0.1-1.5 | Ra=0.8-0.4um |
| C3012 | 0.8 carat | 40°-80° | R0.1-1.5 | Ra=0.4-0.2um |
| C3015Z | 0.8 carat | 40°-80° | R0.1-1.5 | Ra=0.4-0.2um |
| C3035G | 1 carat | 40°-80° | R0.1-1.5 | Ra=0.4-0.2um |
| C3518G | 1.2 carat | 40°-80° | R0.1-1.5 | Ra=0.4-0.2um |
| C4020 | 1.5 carat | 40°-80° | R0.1-1.5 | Ra=0.4-0.2um |
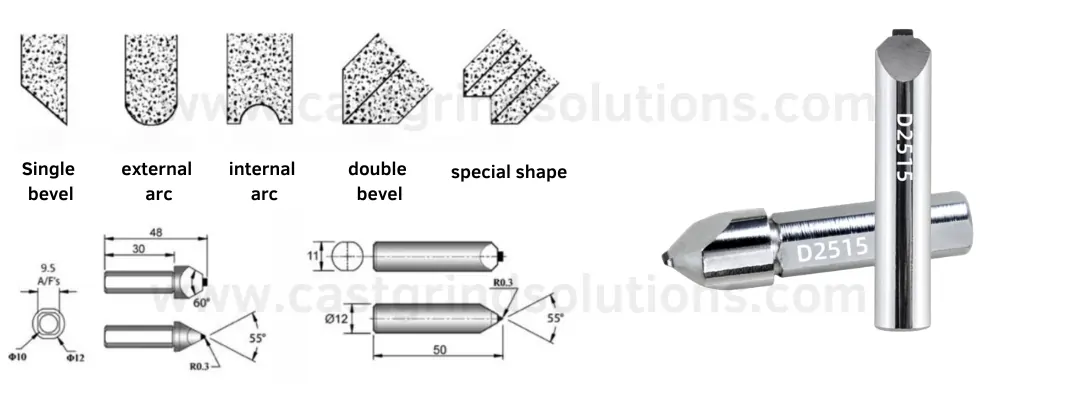
The above three types diamond dressing tools are common models in the market, and we keep them in stock. If you have any special requirements, please contact us. Provide us with the drawings and specifics of your processing needs, and we will offer custom services.
Features
Single Point Diamond Dressers
Let us now explain the single point diamond dresser. The structure of the single point diamond dresser is relatively simple, consisting of a metal handle and a diamond. Single-stone dressers typically use three different types of diamond materials: natural diamond, synthetic single crystal diamond, and polycrystalline diamond. Below, we will first discuss the single tapered point diamond dresser made from natural diamond. The main feature of natural diamond dressers is that each diamond has a unique shape. The inconsistency in shape and sharpness is a characteristic of natural diamond dressers. Natural diamonds are harder than all synthetic diamonds, making them sharper for dressing grinding wheels. They are mainly used for precision dressing of large, hard grinding wheels, such as those required for machining workpieces with a surface roughness of less than Ra0.4um. Additionally, natural diamond dressing tools can dress more workpieces per wheel dressing compared to synthetic diamonds, by at least one-third. For example, if a synthetic diamond dresser can grind 10 workpieces per wheel dressing, a natural diamond dresser can grind at least 15 workpieces. This significantly enhances the sharpness of the grinding wheel and the surface roughness of the workpiece, while reducing the frequency of grinding wheel dressing and improving production efficiency.
Next, we introduce the diamond dresser made from synthetic single crystal diamond. The main feature of these dressers is that the diamond materials are essentially uniform, with regular shapes and sharp edges. Synthetic single crystal diamond is used to replace natural diamond for precision dressing of grinding wheels. While the lifespan of synthetic single crystal diamond is slightly lower than that of natural diamond, its quality is more stable, without significant variations from one piece to another. For instance, the lifespan of diamond dressers made from natural diamond varies by about 20%-30%, and for some lower-quality natural diamond dressers, the lifespan variation can be as high as 50%-60%. In contrast, the lifespan variation of synthetic single crystal diamond dressers is generally controlled within 10%. Therefore, using synthetic single crystal diamond with good shape and structure can significantly reduce customer complaints and loss rates. Currently, 60%-70% of single stone diamond dressers on the market use synthetic single crystal diamond, making it the most ideal replacement for natural diamond.
Lastly, we introduce the diamond dresser made from polycrystalline diamond. Polycrystalline diamond is not a pure diamond material, with diamond purity levels of 50% and 80%. Diamond dressers made from polycrystalline diamond have a triangular working part. The shapes of polycrystalline diamond parts are generally consistent in batch products. These diamond dressers have a relatively narrow application range due to their lower hardness compared to pure diamond materials, making them suitable only for rough dressing of grinding wheels on manual grinders, such as external cylindrical grinders, surface grinders, and rough dressing of 46# grinding wheels. Some 60# grinding wheels with lower dressing precision requirements can also use these diaond dressers. The diameter of polycrystalline diamond dressers ranges from 2mm to 4mm. Their advantage is the lower price, making them the most cost-effective choice for users of manual grinders performing rough grinding. Currently, polycrystalline diamond dressers account for about 10%-20% of the market sales.
The three materials discussed above are the main materials used in single point diamond dressers on the market today.
Below is a summary of the single point diamond dressers based on different uses:
- Natural diamond dressers are mainly used for fine dressing of 80#-120# grinding wheels.
- Synthetic single crystal diamond dressers are mainly used for semi-precision and fine dressing of 60#-80# grinding wheels.
- Polycrystalline diamond dressers are mainly used for rough dressing of 46# grinding wheels.
Precision ranking from high to low:
- Natural diamond
- Synthetic single crystal diamond
- Polycrystalline diamond
Cost-performance ranking from high to low:
- Synthetic single crystal diamond
- Polycrystalline diamond
- Natural diamond
Market share ratios:
- Natural diamond: 10%-20%
- Synthetic single crystal diamond: 60%-70%
- Polycrystalline diamond: 10%-20%
Distributors and customers can decide which material of grinding wheel dressing tool to use or sell based on the grinding wheel parameters. You can also contact us at any time for assistance in selecting the appropriate type.

Diamond Forming Dressers
Dressers for forming, also known as Chisel-type diamond tools, are so named due to the head’s shape, resembling an chisel blade. Since most users have varying handle dimensions, form dresser is primarily custom-made, tailored according to customer drawings or samples. Chisel dressers are mainly used for precision dressing of CNC grinding wheels, such as chamfered wheels, butterfly wheels, and arc wheels.
Forming dressers primarily uses three types of diamond materials: natural diamond, synthetic polycrystalline CVD diamond, and synthetic monocrystalline CVD diamond. CVD stands for chemical vapor deposition, a diamond manufacturing process. Polycrystalline denotes a combination of multiple elements in addition to the main carbon element, such as alloy materials.
Comparison of the three types of diamond materials for forming dressing tools:
Quality Comparison:
Natural diamond > synthetic monocrystalline CVD > synthetic polycrystalline CVD.
Price Comparison:
Natural diamond > synthetic monocrystalline CVD > synthetic polycrystalline CVD.
Cost-Effectiveness:
Synthetic monocrystalline CVD > synthetic polycrystalline CVD > natural diamond.
Stability:
Synthetic monocrystalline CVD > synthetic polycrystalline CVD > natural diamond.
Market Share:
- Synthetic polycrystalline CVD diamond dresser occupies 60%-70%;
- synthetic monocrystalline CVD dressers occupies 20%-30%;
- natural diamond dressers occupies about 5%.
Longevity:
Natural diamond’s actual hardness surpasses that of both CVD monocrystalline and CVD polycrystalline, resulting in the longest lifespan.
Sharpness:
Monocrystalline CVD and natural diamond are roughly equal in sharpness, both about 30%-50% sharper than CVD polycrystalline. These two materials, when used in wheel dressing, result in a higher number of parts ground per dressing compared to CVD polycrystalline. For example, a natural diamond dresser can grind 20 parts per wheel dressing, while a polycrystalline CVD dresser can grind approximately 10-15 parts.
Surface Roughness:
Natural diamond > CVD monocrystalline > CVD polycrystalline.
Natural diamond dressers are mainly used for high-precision dressing below 0.4um, with a high market price. Currently, the market primarily sells CVD monocrystalline and CVD polycrystalline wheel dressers. The most competitive is the CVD monocrystalline dresser, which excels in both cost-effectiveness and stability compared to CVD polycrystalline and natural diamond dressers.
If your current supplier’s grinding wheel dressers are of poor quality or inconsistency, and you need to enhance product competitiveness, please contact us. We can help you select the appropriate type based on your user conditions.
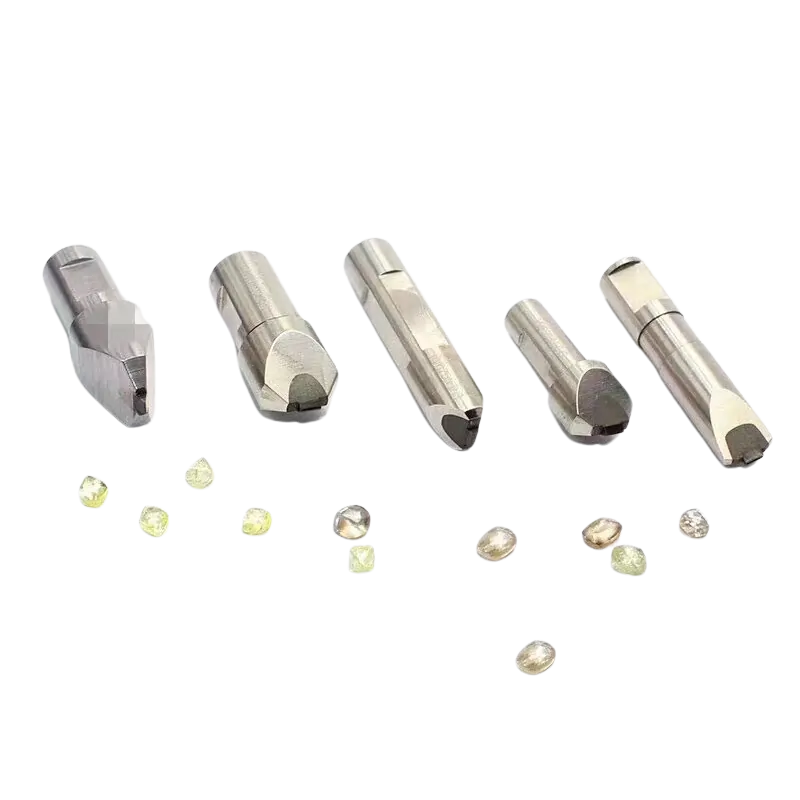

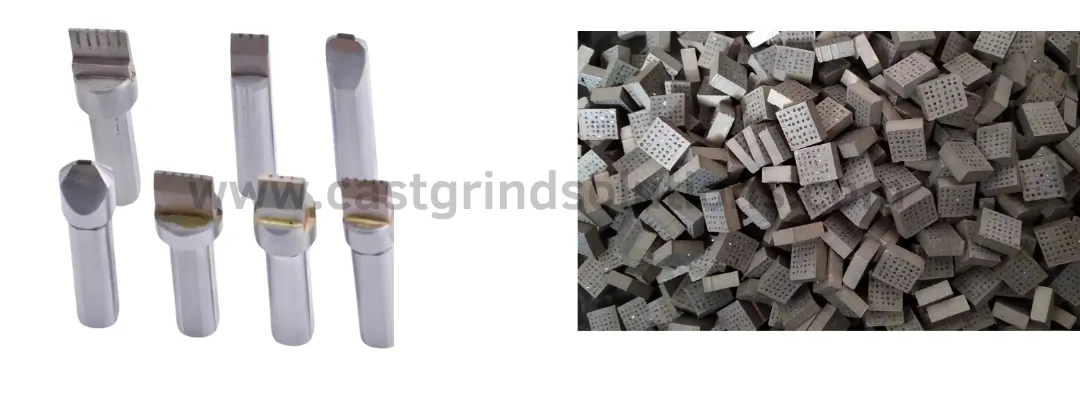
Coarse Grinding Diamond Dressers
In the industry, handle head dressing tool, are also called Impregnated dresser or Multi-point dressers. They are sintered from alloy powder and fine diamond particles. Common shapes are square and round. The sintered diamond grinding wheel dresser has two types: one with a plain surface, where diamond particles are not visible, and one where the particles are neatly arranged on two planes, known as multi-point diamond dressers. The diamond arrangements on square dressers typically have three patterns:
- 6*6: 6 rows and 6 columns of diamond particles per face.
- 5*5: 5 rows and 5 columns of diamond particles per face.
- 4*4: 4 rows and 4 columns of diamond particles per face.
Larger particles are used in the 5*5 arrangement than in the 6*6, and even larger particles in the 4*4 arrangement than in the 5*5. The coarser and larger the diamond particles, the higher the grade, sharpness, and quality of the multi-stone dresser.
The round diamond pen dresser, has a cylindrical head. Among multi-stone dressing tools, square head dressers account for 70%-80% of the market, mainly used for coarse dressing of parallel wheels, such as 46# wheels, or 60# wheels with less stringent dressing precision requirements. The usage of round head dressers is similar to square head dressers, differing only in head shape.
The diamond materials used in these dressers are synthetic monocrystalline diamonds having variations in quality and particle size:
- Coarse Particles: 14-16#, 16-18#, 18-20#.
- Fine Particles: 25-30#, 30-35#, 35-40#, 45-50#.
Coarser particles are more expensive; they impact the grinding wheel dressing in terms of flatness and efficiency:
- Fine diamond particle dressers yield better flatness but lower sharpness.
- Coarse diamond grit dressers provide high efficiency and good sharpness but less flatness.
Therefore, a mixture of particle sizes is often used to maximize performance and adaptability.
Apart from diamond materials, the bonding agent plays a crucial role in the diamond dressers’ lifespan and performance. The bonding agent, mixed with diamonds and sintered together, affects hardness, adhesion, and self-sharpening properties. Coarse grinding involves significant material removal, often exceeding 0.1mm, and occasionally up to 0.5mm. Many operators prefer dry dressing without coolant, challenging the wheel dressers’ toughness and high-temperature resistance. Low hardness results in layer-by-layer shedding, inadequate adhesion leads to easy diamond detachment, and poor self-sharpening causes inadequate wheel dressing.
Our diamond dressers combine ideal diamond material selection, bonding agent formulation, and sintering processes to ensure optimal life span and sharpness, maintaining consistent quality. If your current grinding wheel dressers are of subpar quality or performance, and you aim to boost competitiveness and effectiveness, please contact us for selection guidance or customization.

Application
Applications
Single-point diamond dressers are mainly used in the following fields: automotive parts manufacturing, engine and accessories, mold manufacturing, and various precision machinery parts manufacturing. They are suitable for ordinary cylindrical grinders, centerless grinders, surface grinders, internal grinders, various special-purpose grinders, and some CNC grinders for wheel profiling and grinding. Products with 1.0-carat natural diamonds or above are mainly used in large roll grinders for metallurgy rollers, steel plates, aluminum foils, copper industries, paper industries, etc.
Forming diamond dressers are primarily used in CNC grinders, CNC end cylindrical grinders, CNC internal grinders, crankshaft special grinders, etc. They can dress the wheel’s outer circle, end face, arc, angle, groove, and other complex profiles. They are commonly used in crankshaft manufacturing industries, pistons, internal combustion engines, accessories, reducers, bearings, gears, and other precision components shaping and grinding processes.
Multi-point diamond dressers are mostly applied in automotive parts manufacturing, mold accessories, ship accessories, large railway coal machine engineering machinery, pumps, textile machine accessories, and other precision machinery manufacturing industries. They are suitable for domestic and imported cylindrical grinders, centerless grinders, and surface grinders for wheel dressing. They are also suitable for CNC grinders for end face, angle, R arc, and other complex profile shaping corrections.





