Diamond & CBN Honing Stones
- Ensures accurate hole machining with tight tolerances.
- Results in superior finish and texture on machined parts.
- Extends the life of components through enhanced durability.
- Yielding effective outcomes across a range of materials, including cast iron, carbide, steel, chrome, ceramics, and alloys.
- Parameters and abrasive types can be tailored to specific machining requirements.
Description
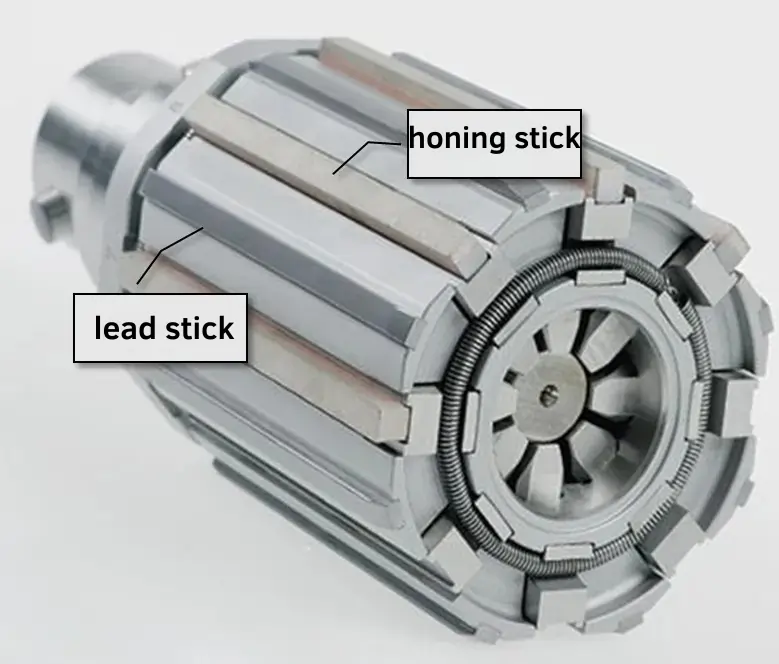
Diamond / CBN Honing Stone(Honing Stick)
Honing, also known as bore finishing, is an efficient surface finishing technique that uses honing stones (honing bars) embedded in the honing head for precision machining of workpiece surfaces. This process is particularly suitable for hole machining, significantly improving surface precision and quality while enhancing wear resistance.
Characteristics of Honing Processing:
Wide Processing Range:
Multi-stone honing tools are mainly used for finishing holes such as cylindrical holes, stepped holes, blind holes, and conical holes. It can also be used for planes, spherical and shaped surfaces, and outer cylindrical surfaces. The diameter of honed holes ranges from 1mm to 1200mm or larger, and the length can reach up to 12000mm. Almost all workpiece materials can be honed.
Excellent Surface Quality:
The honed surface has a cross-hatch pattern, favorable for storing lubricating oil and maintaining the lubricating film, leading to wear resistance and a longer service life. Additionally, since hone speed is much lower than that of conventional grinding, the grinding force and heat are minimal, preventing burns, cracks, alterations, or hardening layers on the workpiece surface.
High Processing Precision:
When honing inner holes, roundness and cylindricity can reach 0.005-0.01mm, and surface roughness can achieve Ra 0.05-0.2μm.
Low Machine Tool Precision Requirements:
Besides using specialized honing machines, honing can also be performed on lathes, boring machines, and drilling machines.
Technical Specifications
Metal Bond Diamond Honing Stones
Common Models:
D46, D54, D64, D76, D91, D107, D126, D151, etc.
In the rough honing stage, metal bond diamond honing sticks with larger grit sizes (such as D151 or D126 diamond honing stones) are often used.
In the semi-finish honing stage, metal bond diamond honing stones with smaller grit sizes (such as D64 or D46 diamond honing stones) are preferred.
Technical Features:
This series of honing stones is made from synthetic diamond and metal bond, mixed, pressed, and sintered. It has high grinding efficiency, low wear rate, ease of use, and good economic benefits.
Applications:
It can meet the high-precision honing requirements such as rough honing, surface honing, and sliding honing.

Metal Bond CBN Honing Stones
Common Models:
D213, D151, D126, D107, D76, D64 D46,D35 etc.
Technical Features:
This series of honing stones is made from CBN and metal bond, mixed, pressed, and sintered. It provides high grinding efficiency, low wear rate, ease of use, and good economic returns.
Applications:
Primarily used for processing quenched cylinder liners (with high hardness, HRC65).
Resin Bond Honing Stones
Common Models:
400#, 500#, 600#, 700#, 800#, 1000#, etc.
Technical Features:
This series of honing stones are made from silicon carbide or diamond and resin bond, mixed, pressed, and sintered.
Applications:
It can meet high-precision honing processes and high-precision honing techniques.

Honing Technical Parameters
- The honing allowance generally does not exceed 0.2mm.
- For steel honing ,the circumferential speed of honing head is about 15-30 meters/min;
- For cast iron or or non-ferrous metals, the circumferential speed can go up to 50 meters/min or more .
- The reciprocating speed of honing should not exceed 15-20 meters/min.
- The pressure of the honing stone on the hole wall is generally 0.3-0.5 MPa, with rough honing up to about 1 MPa, and fine honing less than 0.1 MPa.
- Because the honing stick comes in contact with the workpiece surface area, the vertical pressure of each abrasive grain on the workpiece surface is only 1/50 to 1/100 of that during grinding. Along with low honing speed, the cutting area temperature remains between 50-150℃, reducing residual stress on the machined surface and improving surface quality.
- When processing hardened steel or cast iron, the wear rate of metal-bonded diamond and CBN honing stones is only 1/150 to 1/250 of ordinary sharpening stones. Furthermore, the pressure of the honing stone on the workpiece can be increased by 2 to 3 times, thus improving honing efficiency and surface quality.
Features
Principles and Process of Honing
The core of the honing process lies in its unique machining method. By mounting one or more honing stones on the periphery of the honing head, a radial expansion mechanism (rotary or push type) expands the honing sticks radially to fit tightly against the workpiece hole wall, forming a large-area surface contact. During machining, the honing head mandrel can rotate and reciprocate while the workpiece remains stationary, or the honing head may only rotate while the workpiece reciprocates. This compound motion results in a cutting trajectory of crossed helical lines on the machined surface, ensuring that each abrasive’s path on the hole wall does not repeat, thereby achieving high-precision machining results.
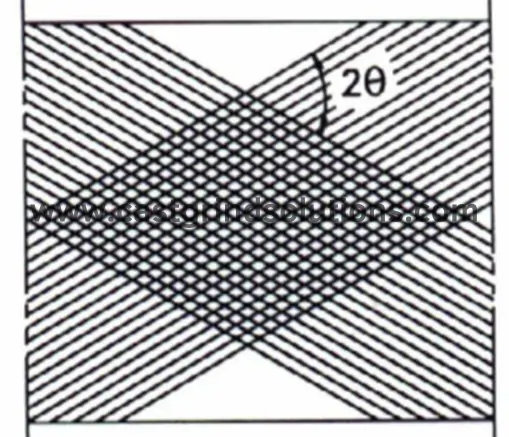
In most cases, the honing mandrel is floatingly connected to the machine spindle or workpiece fixture, allowing the honing head to automatically guide along the workpiece hole wall, reducing reliance on the machine’s precision. During the honing process, the diamond or CBN honing stone and hole wall undergo mutual grinding and self-truing, forming a creation process that further enhances machining precision and surface quality.
Honing Structure and Equipment
The honing head structure typically comprises components such as the body, tapered shaft (adjustment cone), metal bond diamond or CBN honing sticks, and springs. By pushing the tapered shaft downwards, the tapered surface drives the pad blocks radially outward, achieving the honing stone’s radial micro-feed. Advanced honing machines often utilize hydraulic systems to apply constant pressure to the honing stones on the honing head, achieving more precise radial feed and automatic size measurement.
The rotational speed and reciprocating speed of the honing head are key factors affecting machining efficiency and quality. Generally, the mandrel’s rotational speed ranges from 100 to 200 revolutions per minute, and the reciprocating speed ranges from 15 to 20 meters per minute. To flush away chips and abrasives, enhance surface roughness, and reduce cutting zone temperature, a large amount of cutting fluid, such as kerosene or spindle oil with a small amount added, is commonly used during operation. Extreme pressure emulsion is also sometimes used.

Process Characteristics
The honing process features high precision, high surface quality, and long service life. It significantly improves dimensional accuracy, shape accuracy, and reduces surface roughness (Ra value). Honing is widely used for processing materials such as cast iron, hardened and non-hardened steel, and bronze, now also widely used for industrial ceramics, like Zirconia ceramics, alumina ceramics.
In the field of hole machining, the honing process can machine high-precision holes within a diameter range of φ5 to φ500 mm and a depth-to-diameter ratio of up to 10, guided by the centers of pre-machined holes. The machined hole’s surface roughness can reach Ra0.32 to 0.04 micrometers. Hence, the honing process is widely used in mass production for machining critical components such as cylinder bores, hydraulic cylinder barrels, valve bores, and various gun barrels. It can also be used in small batch production to meet different customer customization requirements.
Selection of Honing Tool Materials
The cutting function of the honing process is mainly realized by the diamond or CBN honing stones fixed to the honing head. Therefore, the cutting performance of the diamond honing stone is crucial to the quality and efficiency of honing. The cutting performance of honing sticks depends on their abrasive material, grain size, and bonding agent, ultimately reflected in the stone’s hardness. Properly hard honing stones with good cutting performance ensure fast honing speeds and high efficiency while preventing stone extrusion or breakage.
Common abrasive materials include diamond, cubic boron nitride, corundum, and silicon carbide. Among them, diamond and CBN abrasives are favored for their excellent cutting performance. In the rough honing stage, coarser grit honing stones (e.g., D151 or D126 diamond honing bars) are commonly used; in the semi-finishing stage, finer grit honing stones (e.g., D64 or D46 diamond honing sticks) are chosen; and in the finishing stage, diamond or silicon carbide abrasives (e.g., D30 diamond honing sticks and C30 silicon carbide honing sticks) are preferred for optimal machining results.
Materials for Honing Stones
Honing sticks generally consist of abrasives and bonding agents.
Multy-stone Honing Tools Abrasive Types:
The primary cutting part of honing stone, commonly made from diamond, cubic boron nitride, corundum (including white corundum and brown corundum), and silicon carbide. These materials boast high hardness, high wear resistance, and excellent cutting performance, which effectively remove the workpiece’s surface allowance during honing, improving machining precision and surface quality.
- Diamond and CBN Abrasives: With extremely high hardness and wear resistance, suitable for machining high-hardness materials such as hardened steel and cemented carbide. Diamond and CBN abrasives also exhibit excellent cutting performance and thermal stability, maintaining stable cutting performance during high-speed honing.
- Corundum Abrasives: Including white corundum and brown corundum, with moderate hardness and good cutting performance, suitable for machining cast iron, non-ferrous metals, and other medium-hardness workpiece materials.
- Silicon Carbide Abrasives: With high hardness and brittleness, suitable for machining hard and brittle materials such as glass and ceramics.
Multi-stone Honing Tools Bonding Agents:
Materials that fix abrasives onto the honing stone , commonly including resin, metal, and ceramic. These bonding agents possess varying strengths and wear resistances, meeting different processing conditions’ needs.
- Resin Bonding Agents: With good flexibility and elasticity, adaptable to minor variations in workpiece surfaces, reducing vibrations and noise during processing. Resin bonding agents also exhibit good grinding performance and self-sharpening capability, maintaining abrasive sharpness and enhancing machining efficiency.
- Metal Bonding Agents: With high strength and wear resistance, capable of withstanding significant cutting forces and impacts, suitable for machining high-hardness, complex-shaped workpiece materials.
- Ceramic Bonding Agents: With high hardness and heat resistance, capable of maintaining stable cutting performance under high-temperature conditions, suitable for high-speed honing and dry honing applications.
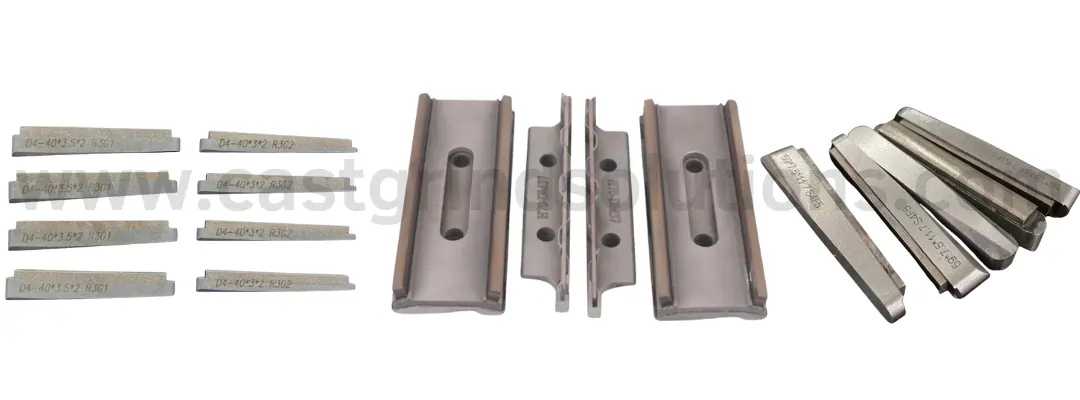

Application
Applications of Sintered Honing Stones
Main Application Areas:
Aerospace:
In the aerospace industry, the requirements for part precision and surface quality are extremely high. Sintered honing stones can be used for machining various high-precision holes, such as those in engine components and fuel systems, ensuring the quality and performance of the parts.
Automobile Manufacturing:
In the automotive industry, sintered honing stones are widely used for the precision machining of critical components such as engine blocks, cylinder sleeves, and connecting rod inner holes. Through honing, the surface quality and wear resistance of the parts can be significantly improved, extending their service life.
Motorcycle Manufacturing:
Similar to automobile manufacturing, motorcycle manufacturing also requires precise machining of key components. Sintered honing stones can be used for hole processing in motorcycle engine blocks, crankcases, and other parts, enhancing the precision and performance of the components.
Other Mechanical Industries:
In industries like construction machinery, petroleum machinery, and hydraulic pneumatics, sintered honing stones are also extensively used for hole processing of various parts. These fields require high precision and wear resistance for their parts, and sintered honing stones can meet these demands.
Typical Application Cases
Engine Block Machining:
During the machining of engine blocks, metal bond honing stones are used for the precise machining of the inner holes of the blocks. By selecting suitable honing parameters and abrasive types, ideal machining effects and surface quality can be achieved.
Automotive Parts Machining:
Automotive parts such as crankshafts and connecting rods also require hole processing. Sintered honing stones can be used for the precision machining of these parts, improving the quality and performance of the components.







